EDITORIAL
DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY
The article analyzes the influence of professional activity of puppeteers on their understanding and manifestation of emotions. We describe the syndrome of inhibited emotional bodily response using factor analysis. This is evidenced by: 1) puppeteers exhibiting a superior capacity to differentiate asthenic emotions compared to a normotypical sample; 2) worse understanding and expression of sthenic spectrum emotions; 3) stereotyped empathy expression with the help of verbal means; 4) minimisation of mimic and motor ways of emotional expression. We assume that puppeteers risk to develop negative consequences from motor and psychological desynchronization of emotional expression in stressful situations. The first assumption is the transformation of the identification strategy with the character into emotional exhaustion. The second is the threat of transition of increased readiness to experience asthenic emotions into depression. Mitigating the adverse effects of suppressed emotional expression in puppeteers may be achieved through psychological support during their professional development.
The purpose of the article is to analyze professional self-actualization and self-regulation in esports at different stages of a professional career. Semi-structured interviews with novice and professional esports athletes and theoretical analysis of scientific literature comprised the methods. This methodology uses A. A. Derkach’s acmeological ideas to examine the problems of professionalism. The research result is the identification of self-regulation and coping ability as a key role in long-term success in esports. Effective programs for training, developing, and supporting esports athletes at all career levels could be further developed using these research results. The research findings have potential utility not only for esports athletes, but also for coaches, psychologists, and experts in acmeology.
RUSSIAN HISTORY
The author examines the pre-war, fifteen-year period of Leningrad’s educational institutions’ activity in training primarily mid-level specialists for the Far North, a period constituting the initial phase of intellectual resource development. The focus is on the organization of vocational training in the second half of the 1920s (the North Group of the Rabfak of the Leningrad University and the Oriental Institute’s Northern Faculty) and the training of personnel in 1930–1941 (the Northern Peoples Institute and the Northern Department of the Hertzen Pedagogical Institute).
GENERAL PEDAGOGY, HISTORY OF PEDAGOGY AND EDUCATION
The article presents the research results of students’ values-based orientations at Surgut State University in the period of 2022–2024. The aim of the work is to identify changes in the hierarchy of students’ values at different stages of education. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of questionnaire data visualized as diagrams is used. The tendencies of shifting priorities from material to existential values are established, age and gender differences are recorded. Based on the results, the necessity of forming programs that promote conscious values-based self-determination among university students is substantiated.
The article focuses on the study of requests for physical activity among schoolchildren representing indigenous minorities of the North, who study and live in boarding schools of Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug – Yugra during the school year. The purpose of the study is to identify the students’ needs for physical activity in extracurricular activities. Sociological data (n = 241) collected in 2023 among students from indigenous minorities of the North underpins the article. By analyzing respondents’ answers, conducting a content analysis, and using statistical information about extracurricular activity programs in educational institutions, we concluded that boarding schools meet pupils’ needs for physical activity. The content of the existing extracurricular activity programs, along with aesthetic, cognitive and spiritual aspects, includes physical culture and sports, which are popular among schoolchildren of all groups. Sports settings in general education institutions reflect the Russian trend towards popularization of physical activity among the population. Several boarding schools (Polnovatskaya and Kazymskaya schools in Beloyarsky District, and Ugutskaya school in Surgutsky District) provided examples for our examination of a systematic approach to involving schoolchildren in sports, particularly northern multiathlon competitions. The needs of pupils in the creation of modern sports infrastructure (on the example of Ugutskaya Secondary School) to meet their motor demands are also revealed. As this research of requests for physical activity is based on the subjective perception of boarding school pupils of the autonomous okrug and is conducted for the first time, it can be useful for heads of educational institutions and teachers engaged in physical development.
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND PROFESSIONAL PHYSICAL TRAINING
The conducted pedagogical research included two interrelated components: a diagnostic and analytical (testing) stage and a practice-oriented module aimed at introducing elements of the sports game “Badminton” in the structure of the physical education elective course. The researchers used comprehensive methods, including pedagogical observation, instrumental diagnostics with InBody and the Cardiovisor cardiological screening system, and mathematical and statistical analysis of the empirical data. One of the significant areas of the research was the study of the student’s body functional state based on the physical health indicators monitoring in pedagogical university. Researchers used individual physical condition maps to provide personalized consultations, recommending corrective foot arch exercises, breathing exercises, and recovery techniques.
The Cardiovisor system analyzed heart rhythm variability, revealing the students’ adaptive abilities levels and specific features of their cardiac vegetative regulation. The organizing phase of the experiment included the comprehensive methodology implementation incorporating badminton lessons, breathing practices and stretching elements. During the academic year, the students of the experimental group mastered the content of the course, aimed at the development of general endurance, coordination abilities, and functional stability of the body. The positive dynamics of the students’ physical condition testifies to the expediency of integrating such a model into educational practice. The scientific substantiation of the proposed method combining the competitive components of the sports game with the restorative-regulatory effects of breathing exercises allows us to consider it as a prospective area in the health-improving system of physical education of students in pedagogical universities.
The relevance of the study is defined by significance of the search for effective means and methods of healthy lifestyle formation in the younger generation of indigenous peoples in Yugra. The solution to this issue is of great importance in the conditions of secondary general education schools with boarding residence of children during the school year. The objective of this research is to evaluate indicators of physical development, functional status, and psychoemotional state among adolescent children of Khanty descent who attend a secondary school’s student health and to establish the organizational and pedagogical prerequisites for a cohesive, health-focused boarding school environment. During the study, we identified somatometric and physiometric indicators of adolescents aged between 13 and 16 years, tested their psychoemotional state (using “Neurosoft”: Spiro-Spectrum, NS-psychotest expert). The analysis of the results led to the conclusion that it is necessary to develop programs aimed at creating a unified health-forming space of the boarding school, ensuring the preservation of a high level of physical and mental health in children, the formation of their value attitude to a healthy lifestyle.
METHODOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGY OF PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
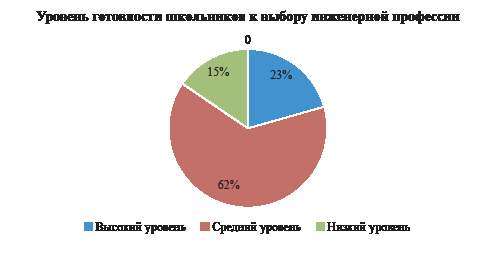
The relevance of the article is determined by engineering professions’ increasing demand given rapid technological progress. The demand for qualified specialists is increasing in various industries, from information technologies to mechanical engineering. However, many high school students face challenges in choosing a career. The article analyzes the willingness of high school students to choose an engineering profession, as well as the factors that influence this process.
The article presents the research results on the development and approbation on the methodology of financial literacy development in pedagogical education undergraduates at university. The structural and conceptual model of financial literacy development, including purpose, content, procedural and result blocks, is reviewed. We propose and experimentally test the pedagogical conditions for effective financial literacy development. These include integration of thematic blocks on the development of educational games on financial topics in the academic discipline “Methodology of teaching financial literacy”, creation of a motivational educational environment through the use of interactive teaching methods, project activities and active inclusion of students in educational activities on financial literacy for different categories of education through the participation in the Regional forum “Financial literacy for everyone”. The results of the research indicate significant positive changes in the level of motivational, cognitive and activity components of students’ financial literacy in the experimental group compared with the control group.
Relevance of the article is determined by the increasing necessity of forming the culture of self-governance among university students in the conditions of digitalization. The modern educational environment places new demands on the personality of students, including the development of the ability to independently organize educational and professional activities. Digitalization of the educational process, along with its advantages, poses challenges for students to adapt to new learning formats and time management, which requires special self-management skills. The aim of the article is to theoretically examine self-governance culture as a key element of the educational process and analyze its formation in the conditions of digital educational environment. The authors organize modern approaches to understanding the essence and structure of self-governance culture, its influence on the personal and professional development of students. The essence of the self-governance culture is revealed, which consists in the formation of skills of self-organization, selfregulation and self-realization of students. The key pedagogical conditions promoting the development of selfgovernance, including the use of digital platforms, adaptive learning systems and active learning methods are classified. It is proposed to use the integration of digital technologies and pedagogical strategies to improve the effectiveness of the educational process. It is proved that the educational environment of universities has a significant resource potential for the formation of self-governance skills. Teachers, psychologists, researchers in the field of education, as well as heads of educational organizations interested in improving the quality of students’ education and their professional success are target audience of the article.